Wastewater treatment is essential for maintaining environmental sustainability and managing water resources efficiently, particularly in Malaysia, where rapid urbanization has led to increased demand for clean water. One of the most effective and widely used methods in wastewater treatment is the activated sludge system. But what is an activated sludge system, and how does it function? This blog provides a detailed look at this innovative system, highlighting its process, advantages, and significance in Malaysia’s wastewater management.
What Is an Activated Sludge System?
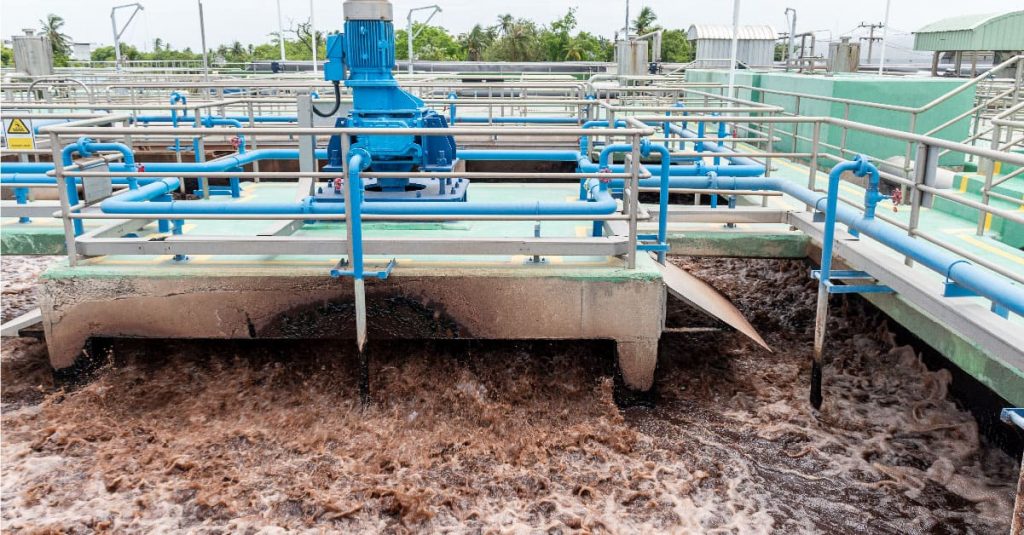
An activated sludge system is a biological wastewater treatment process that uses microorganisms to break down organic pollutants in wastewater. The process involves aerating a mixture of wastewater and activated sludge, a dense mixture of microorganisms and suspended solids, to remove organic matter efficiently. This treated water is then separated from the sludge, which is either recycled back into the system or further processed.
The conventional activated sludge system is the most commonly used version of this technology. It has become a key component in wastewater treatment plants across Malaysia, offering a reliable and efficient solution for managing both domestic and industrial wastewater.
How the Activated Sludge System Works?
- Influent Entry
Raw wastewater enters the aeration tank, where it is mixed with activated sludge. - Biological Treatment
The aeration process provides oxygen to the microorganisms, enabling them to decompose organic pollutants into carbon dioxide, water, and other byproducts. - Settling Phase
The aerated mixture flows into the secondary clarifier, where gravity separates the activated sludge from the treated water. - Sludge Management
A portion of the settled sludge is recycled into the aeration tank, while the rest is sent for further processing or disposal. - Effluent Discharge
The treated water is either discharged into natural water bodies or undergoes additional treatment for reuse in industrial or agricultural applications.
Advantages of the Activated Sludge System
- High Efficiency
The activated sludge system is highly effective in removing organic pollutants, ensuring high-quality effluent suitable for discharge or reuse. - Flexibility
This system can adapt to varying wastewater compositions and volumes, making it suitable for diverse applications across Malaysia. - Sustainability
By promoting resource recovery and reducing pollution, the sludge system supports Malaysia’s sustainability goals. - Cost-Effectiveness
The conventional activated sludge system is cost-effective for large-scale wastewater treatment, as it can handle significant volumes with minimal operational issues.
The Role of the Activated Sludge System in Malaysia
Malaysia’s wastewater treatment plants rely heavily on the activated sludge system to manage domestic and industrial wastewater. With increasing environmental regulations and the need for sustainable water management, the conventional activated sludge system has proven to be a reliable solution.
The system plays a pivotal role in:
- Protecting Water Resources
By treating wastewater effectively, it prevents pollutants from contaminating rivers, lakes, and coastal areas. - Supporting Industrial Growth
Industries can rely on the sludge system to treat their effluent, ensuring compliance with environmental standards while maintaining operational efficiency. - Promoting Water Reuse
Treated wastewater is increasingly being reused for irrigation, landscaping, and industrial processes, reducing pressure on freshwater resources.
Activated Sludge Process by Ion Exchange: Efficient Biological Wastewater Treatment
The Activated Sludge Process is a widely used biological wastewater treatment method that utilizes an aeration tank containing suspended microorganisms, known as Mixed Liquor Suspended Solids (MLSS), to break down the organic matter present in the effluent. The treated water then moves to a secondary clarifier, where the MLSS settles, and the sludge is partially recirculated back into the aeration tank to maintain microbial activity. Oxygen or air is supplied through either surface or diffused aeration systems to sustain the microorganisms. The process operates with a Hydraulic Retention Time (HRT) of approximately 6–7 hours and a Sludge Retention Time (SRT) ranging from 8–15 days, ensuring effective organic matter degradation and wastewater purification.
With Ion Exchange’s advanced treatment solutions, industries can achieve superior wastewater management, enhanced efficiency, and environmental compliance.
Conclusion
The activated sludge system is a cornerstone of Malaysia’s wastewater treatment infrastructure. Its ability to treat large volumes of wastewater efficiently, combined with its adaptability and sustainability, makes it indispensable for addressing the country’s water management challenges. Understanding what an activated sludge system is and how it functions underscores its significance in protecting the environment and promoting water reuse.
Connect with Ion Exchange experts today and take a step toward a more sustainable future.