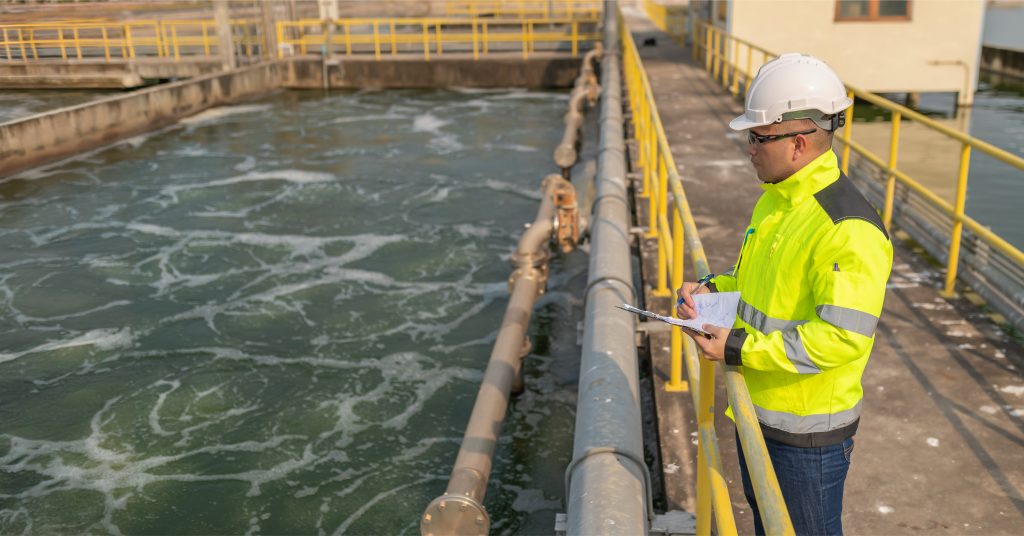
Water quality in Malaysia is a critical issue that has far-reaching implications for public health, agriculture, and the environment. As Malaysia continues to urbanize and industrialize, the strain on its water resources intensifies, leading to significant challenges in maintaining clean and safe water supplies. The purpose of this blog is to highlight the key issues affecting water quality in Malaysia, examine the Malaysia water quality standard, and explore the causes and impacts of water hardness in Malaysia.
Overview of Water Quality in Malaysia
The current state of water quality in Malaysia presents a complex picture. Rapid industrialization, urbanization, and agricultural activities have introduced various pollutants into Malaysia’s water bodies, degrading the overall water quality in Malaysia. These pollutants include heavy metals, pesticides, nitrates, and industrial effluents, which are often discharged directly into rivers and lakes without adequate treatment.
Water sources in Malaysia, such as rivers, lakes, and groundwater, are particularly vulnerable to pollution due to the country’s high population density and economic activities. For example, the Klang River in Kuala Lumpur is infamous for its high levels of contamination, primarily from industrial waste, sewage, and runoff from urban areas. Similarly, agricultural runoff in rural areas has led to elevated levels of nitrates and phosphates in water bodies, contributing to eutrophication and the degradation of aquatic ecosystems.
The challenges to maintaining high water quality in Malaysia are compounded by the country’s tropical climate, which includes heavy rainfall and frequent floods. To address the issues of water pollution, the Malaysian government has established a set of guidelines known as the Malaysia water quality standard. The Malaysia water quality standard outlines specific parameters that must be monitored and maintained, such as pH, turbidity, dissolved oxygen, and the presence of chemical contaminants like heavy metals and pesticides.
Water Hardness in Malaysia: Causes and Impacts
One specific issue related to water quality in Malaysia is water hardness. Water hardness in Malaysia is primarily caused by the presence of dissolved minerals, particularly calcium and magnesium, in the water supply. These minerals are naturally occurring and enter the water through the dissolution of limestone and other geological formations. However, industrial activities, such as mining and manufacturing, can also contribute to elevated levels of hardness in water by introducing additional minerals into water bodies.
The impact of water hardness in Malaysia is multifaceted. In households, hard water can cause scaling in pipes, water heaters, and appliances, leading to reduced efficiency and increased maintenance costs. For consumers, hard water can reduce the effectiveness of soap and detergents, leading to higher consumption of these products. In industrial settings, water hardness can have more serious consequences. In manufacturing processes that require high-quality water, such as electronics or pharmaceuticals, water hardness can compromise product quality and lead to costly production disruptions.
Key Issues Affecting Water Quality in Malaysia
Several key issues are affecting water quality in Malaysia, contributing to the ongoing challenges of maintaining clean and safe water supplies:
- Industrial Pollution: The rapid growth of manufacturing and industrial activities in Malaysia has led to the discharge of untreated or inadequately treated industrial waste into rivers and lakes.
- Agricultural Runoff: The use of chemical fertilizers, pesticides, and herbicides in agriculture contributes to the contamination of water bodies.
- Urbanization and Waste Management: Inadequate sewage treatment and improper disposal of solid waste contribute to the contamination of water sources with pathogens, nutrients, and other pollutants.
- Deforestation and Soil Erosion: The increased sediment load reduces water quality by introducing suspended solids, which can carry attached pollutants and disrupt aquatic ecosystems.
- Climate Change: Changing weather patterns, including more intense rainfall and longer dry periods, exacerbate water quality issues in Malaysia.
- Mining Activities: Mining operations, especially for tin, gold, and other minerals, contribute to water pollution through the release of heavy metals and sediment into nearby water bodies.
- Overexploitation of Water Resources: The overuse of groundwater and surface water for agriculture, industry, and domestic use can lead to the depletion of water resources, reducing the natural ability of ecosystems to purify water and leading to increased concentrations of pollutants.
Ion Exchange: Elevating Water Quality Standards in Malaysia
-
INDION LAMPAK
INDION Lampak, developed by Ion Exchange, is a compact and modular unit tailored to meet the drinking water demands of communities and industrial applications. It combines a pump, static mixer, flocculation, lamella clarifier, gravity sand filter, and chemical dosing systems to produce disinfected water with less than 5 mg/l TSS from feed water containing up to 500 mg/l TSS. Easy to operate and low-maintenance, INDION Lampak can be powered by a diesel generator or renewable energy, making it ideal for regions without electricity. Its lightweight, corrosion-resistant materials and space-efficient design ensure easy transport, operation, and upkeep.
-
INDION NEW GENERATION IRON REMOVAL FILTER (NGIRF)
INDION NGIRF is an advanced solution for removing dissolved iron, typically found as ferrous bicarbonate in groundwater. Utilizing a catalytic oxidation process, this filter efficiently reduces iron levels to below 0.3 ppm without the need for chemicals. Designed with convenience in mind, it features a corrosion-resistant Fiber Reinforced Plastic (FRP) pressure vessel and PVC pipes. Pre-assembled and tested, the NGIRF comes equipped with user-friendly valves, offering a reliable and easy-to-operate solution for treating water with high iron content.
-
INDION Water Potability Test Kit
INDION Water Potability Test Kit is a versatile tool designed to measure eight essential chemical parameters of drinking water as per the Bureau of Indian Standards. Providing quick and accurate results for pH, total hardness, alkalinity, chloride, fluoride, chlorine, iron, and nitrate, this kit is user-friendly and ideal for semi-skilled individuals, offering an affordable way to ensure safe drinking water.
-
INDION Packaged Sewage Treatment Plants
INDION Packaged Sewage Treatment Plants offer decentralized sewage treatment in a compact, single-tank design that produces low sludge volumes and requires minimal electricity, making them highly cost-effective. Available in capacities ranging from 10 to 100 m³/d, these systems are ideal for smaller needs, while advanced options like Fluidized Media Reactor (FMR), Moving Bed Biofilm Reactor (MBBR), and Membrane Bio-Reactor (MBR) processes are available for efficiently handling higher flow rates in larger applications.
Conclusion
The quality of water in Malaysia is under significant pressure from a range of human activities and environmental factors. Adhering to the Malaysia water quality standard is essential for protecting public health, preserving ecosystems, and ensuring the sustainable use of water resources. Addressing the issue of water hardness in Malaysia is also crucial, as it impacts both household and industrial water users.