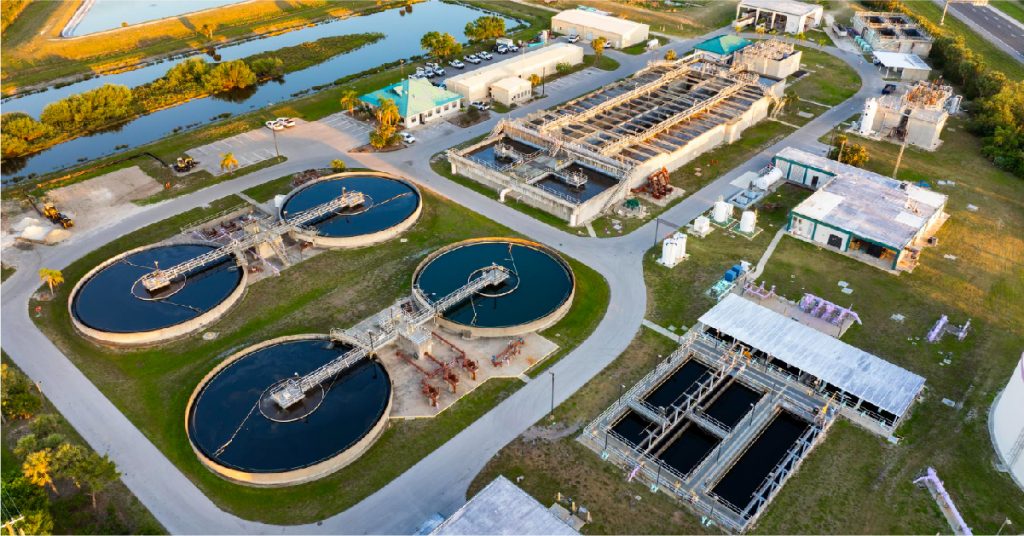
As Malaysia continues to urbanize and industrialize, the demand for clean water is rising at an unprecedented pace. At the same time, climate variability, population growth, and pollution are placing increasing stress on natural freshwater resources. In this evolving landscape, municipal wastewater is no longer viewed as waste alone—it is becoming a valuable resource. Through advanced treatment and reuse, cities across Malaysia can secure sustainable water supplies while protecting the environment.
The Growing Importance of Municipal Wastewater Treatment
Every day, urban centers generate large volumes of municipal wastewater from households, commercial buildings, institutions, and public facilities. Traditionally, this wastewater was treated only to meet discharge standards before being released into rivers or the sea. Today, the focus is shifting toward recovery and reuse.
Modern municipal wastewater treatment not only removes contaminants but also transforms wastewater into a dependable source of water for non-potable applications such as irrigation, industrial processes, landscaping, cooling systems, and groundwater recharge. This approach directly supports Malaysia’s water security and sustainability goals.
Challenges Facing Urban Wastewater Management in Malaysia
Despite progress, municipal authorities face several key challenges:
- Rapid Urban Growth – Increasing volumes of wastewater put pressure on existing infrastructure.
- Environmental Compliance – Stricter discharge regulations require higher treatment performance.
- Water Scarcity in Certain Regions – Seasonal shortages make alternative water sources essential.
- Operational Costs – Energy, chemicals, and sludge management impact long-term affordability.
To overcome these challenges, cities need advanced municipal wastewater treatment systems that are efficient, scalable, and environmentally responsible.
Innovations in Municipal Wastewater Treatment Systems
Technological innovation is redefining how wastewater is treated and reused in Malaysia. Key advancements include:
1. Membrane-Based Treatment
Membrane bioreactors (MBR), ultrafiltration, and reverse osmosis enable superior removal of suspended solids, pathogens, and dissolved contaminants. These systems deliver high-quality effluent suitable for reuse in industry and urban utilities.
2. Advanced Biological Processes
Modern biological treatment technologies enhance organic load reduction while minimizing sludge generation. These processes improve overall plant efficiency and reduce operating costs.
3. Smart Automation and Monitoring
Digital control systems, sensors, and SCADA platforms provide real-time monitoring of flow, water quality, and energy usage. This allows operators to optimize performance, detect faults early, and ensure regulatory compliance.
4. Resource Recovery and Circular Water Use
Innovative systems now focus on recovering water, energy, and nutrients from wastewater. Treated effluent is reused, biogas is generated from sludge, and valuable by-products are reclaimed—supporting a circular economy.
Role of Municipal Wastewater Treatment Chemicals
Even with advanced equipment, municipal wastewater treatment chemicals remain essential for process efficiency and stability. They support critical functions such as:
- Coagulation and flocculation for effective solid-liquid separation
- pH control and neutralization
- Odor control and biological activity enhancement
- Sludge conditioning and dewatering
Ion Exchange offers a comprehensive range of environmentally responsible chemicals designed to improve treatment efficiency while minimizing chemical consumption and sludge volumes.
Ion Exchange’s Expertise in Municipal Wastewater Solutions
Ion Exchange has been at the forefront of designing and implementing municipal wastewater treatment systems across Asia, including Malaysia. Our integrated solutions combine engineering, advanced process technologies, and high-performance treatment chemicals.
Water Assurance with Packaged Systems
A major problem faced by housing and commercial complexes, hotels, resorts, hospitals, academic institutions, and malls is the availability of a regular water supply; many of them are dependent on tanker water. Recycling of sullage and sewage using decentralised packaged sewage treatment systems provides an effective and reliable solution to help augment the water supply and relieve water shortage.
Ion Exchange offers a range of packaged sewage treatment technologies, which include bio-reactor (MBR), sequential batch reactor (SBR), moving bed bio-reactor (MBBR), and an advanced version ofthe attached growth process (NGPST). While selecting the treatment technology, the following points need to be considered:
- End Use
- Capital Cost
- Operating Cost
- Area Available
- Life Cycle Cost
- Location
- Quantity of Sewage
If the quantity of sewage to be treated is >1 MLD, moving bed bio-reactor or sequential batch reactor are preferred options. However, while capital cost is lower, the quality of treated sewage is suitable for low-end purposes such as flushing, gardening, and in some cases even as cooling tower make-up, after appropriate tertiary treatment. For treating smaller quantities of sewage, such as in small housing complexes, organic effluentfroms canteens and washrooms, the advanced process (NGPST) is more suitable as it is compact, user-friendly, and minimizes the use of power and chemicals to treat and reuse sewage.
Managing Sewage Sludge
Sludge or residual solids are the by-product of biological or physico-chemical processes or sewage treatment. As more sewage treatment plants (centralised and decentralised) are installed, a greater quantity of sludge is generated, and sludge disposal will become a concern. Thus, sludge management is essential. However, technologies to condition, treat, and manage sludge are widely available.
The most cost-effective treatment process for sewage sludge treatment is anaerobic digestion, in which, apart from treating sludge, generates biogas which can be used as a source of heat and power. The process of anaerobic sludge digestion also produces organic fertiliser.
Benefits of Municipal Wastewater Reuse in Malaysia
- Water Security – Reduces dependence on natural freshwater sources
- Environmental Protection – Minimizes pollution of rivers and coastal ecosystems
- Cost Efficiency – Lowers long-term water procurement and treatment costs
- Urban Resilience – Ensures stable water availability during droughts or peak demand
- Sustainability Compliance – Aligns with national and regional environmental goals
Conclusion
The future of urban water management in Malaysia lies in transforming municipal wastewater into a reliable and sustainable resource. Through advanced municipal wastewater treatment, innovative municipal wastewater treatment systems, and optimized use of municipal wastewater treatment chemicals, cities can achieve higher efficiency, environmental protection, and long-term water security.
With Ion Exchange’s proven expertise and integrated solutions, Malaysian municipalities are well positioned to embrace wastewater reuse as a cornerstone of sustainable urban development.